If you have good hearing, it’s easy to take it for granted. But if you’re one of the 36 million people that suffer from hearing impairments, you know first-hand that hearing loss is difficult to live with.
Hearing loss can negatively affect your social and emotional wellbeing due to the inability to understand and follow conversations. Hearing loss can become a roadblock at work, in relationships, and during enjoyable activities such as concerts and parties.
Hearing loss can occur for a number of reasons including age, illness, and genetics, and it is currently the third most common health problem in the U.S. But exponential hearing loss doesn’t have to be an accepted part of aging.
It’s important to catch hearing loss early in order to prevent deterioration. At WWMG, our Audiologist specializes in the evaluation, diagnosis, treatment, and management of hearing loss and balance disorders in families throughout all stages of life.
We offer a comprehensive hearing evaluation to help patients understand the full impact and causality of their hearing loss. Taking a comprehensive hearing evaluation early can give you a clear understanding of the health of your hearing, and help you manage and prevent further hearing loss.
What’s Involved in a Comprehensive Hearing Evaluation
A WWMG comprehensive hearing evaluation is a non-invasive hearing test that is performed by an Audiologist.
Here’s what you can expect during a comprehensive hearing evaluation at WWMG:
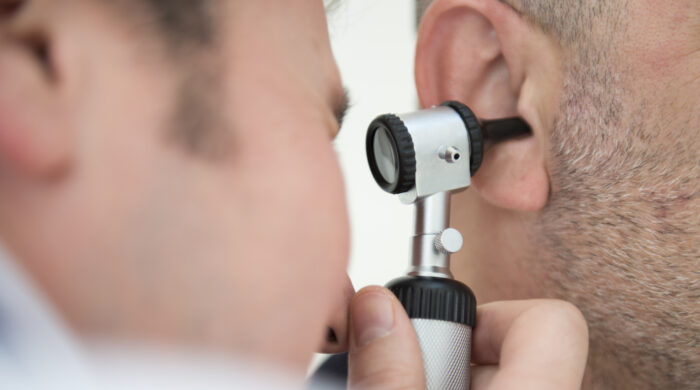
- The Audiologist will begin by inspecting your eardrums with an otoscope.
- Next, you will put on a pair of earphones in a soundproof test booth, where you will listen and respond to a series of sounds of descending volume.
- At times you will be given prompts to raise your hand, push a button, or repeat what you heard through the earphones.
- Your hearing thresholds for each pitch and ear are recorded throughout the test on a graph called an audiogram.
- In addition to this test, your Audiologist may recommend further testing to gauge the health of your middle ear and inner ear function.
Types of Hearing Loss
If you suspect you may have hearing loss, have been diagnosed with hearing loss, or if you are considering visiting us at WWMG for a comprehensive hearing evaluation, it may be helpful to have a basic understanding of hearing loss. There are three types of hearing loss.
- Conductive Hearing Loss – Due to problems with structures in the ear such as the ear canal, eardrum, or the bones in the middle ear.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss – Nerve-related hearing loss in the inner ear.
- Mixed Hearing Loss – a combination of Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss due to structural damage to the inner, middle, outer ear, or damage to the auditory nerve.
Causes of Hearing Loss
While there are many causes of hearing loss, the most common indicator of hearing loss is age. Age-related hearing loss is believed to be a product of genetics and/or lifetime exposure to damaging elements such as noise and medications.
Noise
Exposure to loud noise can damage sensitive structures in the inner ear, leading to noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). NIHL can be temporary or permanent, in one or both ears. Without proper ear protection, loud construction sites, headphone use, concerts, and even vacuuming have the potential to damage hearing, especially when exposure is consistent. NIHL is preventable, and wearing ear protection and/or avoiding loud noise whenever possible, will help preserve your hearing.
Medications
Some medications have a history of damaging the inner ear, leading to impaired hearing or balance. Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) and vertigo are common symptoms of medication-induced hearing loss. Common medications such as large doses of Asprin have been known to cause hearing loss. Learn more about medications that can cause hearing loss here, and stay alert. If you have sudden or unexplained hearing loss after starting a new medication, report it to your physician.
Genetics
Some forms of hearing loss are caused by genetic mutations, and passed down through generations. It is estimated that age-related hearing loss is 35-55% genetic.
Talk to your physician about taking a comprehensive hearing evaluation if you experience any changes in your hearing, as hearing loss can also be a symptom of these and other serious problems such as ear infections, allergies, head trauma, middle ear fluid, tumors, Multiple Sclerosis, or Meniere’s disease.
Signs You May Have Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is oftentimes irreversible, so it’s important to protect your ears. However, because hearing loss typically occurs gradually over time, it’s not always easy to identify it before it becomes a problem. Some symptoms of hearing loss include:
- Difficulty maintaining a conversation in noisy environments such as restaurants, sidewalks, and in cars.
- People seem to mumble all the time.
- People around you need to repeat themselves often.
- Difficulty hearing people when they aren’t facing you, or when they call for you from another room.
- Ringing or buzzing in your ears.
If this list of symptoms sounds familiar, take this more complete online hearing test to see if you should talk to your physician about getting tested for hearing loss.
If you or someone you know believes they may be experiencing hearing loss, talk to your primary care provider about being referred to the WWMG Audiology department for a comprehensive hearing evaluation.